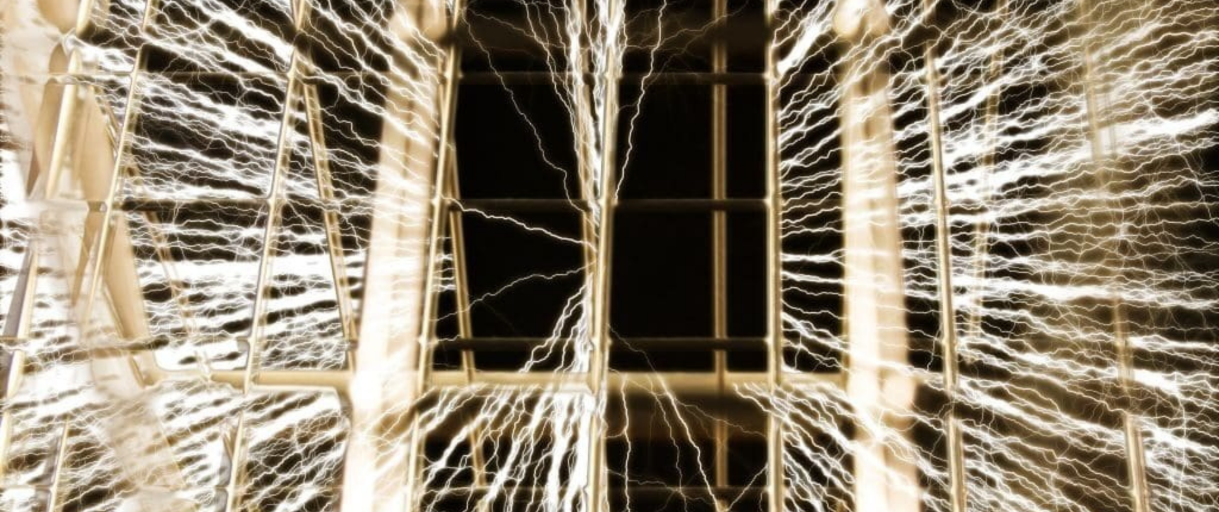
If you are wondering what is a Faraday cage, you should know that a Faraday cage, named after the British scientist Michael Faraday who first demonstrated its principles in 1836, is an enclosure made of conductive material that blocks external electric fields and electromagnetic waves from penetrating its interior. This shielding effect occurs because the conductive material redistributes electric charges on its surface in response to external electric fields, effectively neutralizing the field within the enclosed space. Faraday cages are utilized in various applications to protect sensitive electronic equipment, safeguard individuals from electrical hazards, and prevent unauthorized access to electronic signals.
Principle of Operation for the Faraday Cage
Before we discuss what is a Faraday cage, we have to tackle the basics. The fundamental principle behind a Faraday cage involves electrostatic shielding. When an external electric field impinges upon the conductive material of the cage, free electrons within the conductor move to counteract the field’s influence. This redistribution of charge creates an opposing electric field that cancels the external field within the enclosure. As a result, any electronic devices or individuals inside the cage are shielded from external electric fields and electromagnetic radiation. It’s important to note that while Faraday cages are effective against electric fields, their ability to block magnetic fields, especially low-frequency ones, is limited. To enhance effectiveness against varying electromagnetic fields, factors such as the conductivity, thickness, and permeability of the cage material, as well as the size of any apertures, are optimized. (Source)
Historical Context
 You might also want to know about the historical context besides what is a Faraday cage. Michael Faraday’s experiments in the 19th century laid the groundwork for understanding electromagnetic shielding. In 1836, Faraday demonstrated that a conductive enclosure could block external electric fields, leading to the development of the Faraday cage concept. His work built upon earlier observations by scientists such as Jean Antoine Nollet in 1754 and Benjamin Franklin in 1755, who noted that electric charges reside on the exterior of conductors and do not influence contents within. Faraday’s systematic studies provided a deeper understanding of electrostatic shielding, leading to practical applications in various fields.
You might also want to know about the historical context besides what is a Faraday cage. Michael Faraday’s experiments in the 19th century laid the groundwork for understanding electromagnetic shielding. In 1836, Faraday demonstrated that a conductive enclosure could block external electric fields, leading to the development of the Faraday cage concept. His work built upon earlier observations by scientists such as Jean Antoine Nollet in 1754 and Benjamin Franklin in 1755, who noted that electric charges reside on the exterior of conductors and do not influence contents within. Faraday’s systematic studies provided a deeper understanding of electrostatic shielding, leading to practical applications in various fields.
Applications of Faraday Cages
Faraday cages serve multiple purposes across different domains:
-
Protecting Electronic Equipment: Sensitive electronics, such as radio receivers and computers, are susceptible to electromagnetic interference (EMI) that can disrupt their operation. Faraday cages are used to shield these devices from external EMI, ensuring reliable performance. You can easily use a DIY Faraday cage for such a project.
-
Safety from Electric Hazards: In environments where high-voltage equipment operates, Faraday cages provide safety by preventing accidental contact with live electrical components. The conductive enclosure directs electric currents around the exterior, protecting individuals inside.
-
Preventing Signal Interception: Faraday cages are employed to prevent unauthorized access to electronic signals. For example, in secure facilities, rooms are lined with conductive materials to block external attempts to intercept communications or data transmissions.
-
Electromagnetic Compatibility Testing: Manufacturers use Faraday cages, often referred to as shielded rooms, to test electronic devices for compliance with electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) standards. These controlled environments allow for accurate assessment of a device’s susceptibility to and emission of electromagnetic interference.
Limitations of the Faraday Cage

AI illustration of a Faraday Cage in action
While Faraday cages are effective in blocking electric fields and certain electromagnetic waves, they have limitations:
-
Magnetic Field Penetration: Faraday cages are less effective against static or low-frequency magnetic fields. For instance, the Earth’s magnetic field can penetrate a Faraday cage, meaning devices like compasses will function normally inside.
-
Design Considerations: The effectiveness of a Faraday cage depends on its design, including the conductivity and thickness of the material used, the presence of any gaps or holes, and whether the cage is grounded. For high-frequency applications, the size of apertures must be smaller than the wavelength of the incident electromagnetic waves to ensure effective shielding.
Modern Relevance
In today’s technologically driven world, Faraday cages continue to play a crucial role:
-
Personal Electronics Protection: With the proliferation of personal electronic devices, there is a growing concern about electromagnetic radiation exposure. Some individuals use small Faraday pouches or boxes, often referred to as “Faraday bags,” to block signals from devices like smartphones, preventing tracking and unauthorized data access. However, it’s important to note that while these bags can block certain signals, they are not foolproof and may not protect against all forms of electromagnetic radiation.
-
Security Measures Against Signal Theft: Criminals have attempted to exploit Faraday principles for illicit activities. There have been instances where individuals used Faraday-lined bags to shield stolen items from electronic article surveillance (EAS) systems in retail settings, attempting to bypass security measures. For example, in La Rioja, Spain, two men were arrested for using Faraday-lined bags to steal high-value cosmetic products.
-
Ensuring Data Security: Organizations concerned about data breaches and electronic eavesdropping employ Faraday cages to protect sensitive information. By creating a controlled electromagnetic environment, they reduce the risk of unauthorized data interception and ensure the integrity of confidential communications.
So What Is A Faraday Cage?
A Faraday cage is a fundamental concept in electromagnetism, providing effective shielding against electric fields and certain electromagnetic waves. Its applications range from protecting electronic equipment and ensuring personal safety to securing sensitive data and maintaining privacy. Understanding the principles and limitations of Faraday cages is essential in our increasingly electronic world, where managing electromagnetic interference and protecting against unauthorized signal interception are paramount.
You may also like:
How To Make Black Powder At Home (Video)